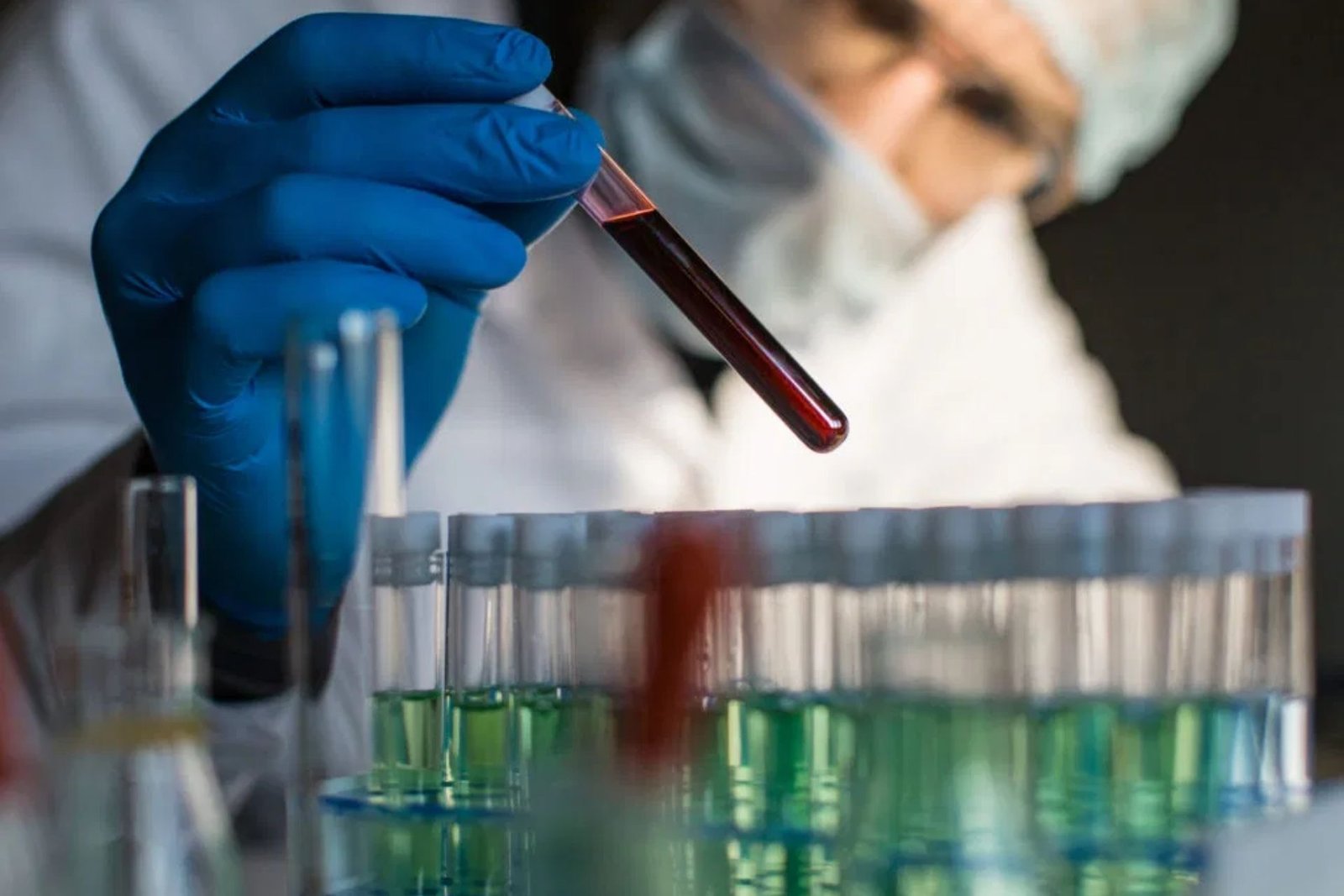
A straightforward blood test that can recognize in excess of 50 kinds of malignancy before any clinical signs or indications of the sickness is sufficiently precise to be carried out as a multi-disease screening test, as per researchers.

The test, which is additionally being guided by NHS England, is focused on individuals at higher danger of the infection, including patients matured 50 years or more established. It can distinguish numerous kinds of malignancy that are hard to analyze early, like head and neck, ovarian, pancreatic, oesophageal and some blood tumors.
Researchers said their discoveries, distributed in the diary Annals of Oncology, shows the test precisely identifies malignant growth, regularly before any signs or side effects, while having a low bogus positive rate.
Dr Eric Klein, director of the Glickman Urological and Kidney Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, US, and first creator on the paper, said: “Discovering malignancy early, when therapy is bound to be effective, is quite possibly the main chances we need to decrease the weight of disease. “These information recommend that, whenever utilized close by existing screening tests, the multi-malignant growth discovery test could significantly affect how disease is distinguished and, at last, on general wellbeing.”
The test, created by US-based organization Grail, searches for synthetic changes in sections of hereditary code – sans cell DNA (cfDNA) – that break from tumors into the bloodstream.Scientists researched the presentation of the test in 3,537 individuals – 2,823 individuals with disease and 1,254 individuals without. It accurately recognized when malignant growth was available in 51.5% of cases, across all phases of the illness, and wrongly identified disease in just 0.5% of cases.

In strong tumors that don’t have any screening alternatives -, for example, oesophageal, liver and pancreatic malignancies – by and large affectability (the capacity to create a positive aftereffect) of the test was twice (65.6%) as that for strong tumors that do have screening choices, like bosom, entrail, cervical and prostate diseases. In the interim, the general affectability in malignant growths of the blood, like lymphoma and myeloma, was 55.1%. The test accurately likewise recognized the tissue in which the malignant growth was situated in the body in 88.7% of cases.
Dr Klein said: “We accept that malignancies that shed more DNA into the circulatory system are identified all the more without any problem.
“These malignancies are likewise bound to be deadly, and earlier examination shows that this multi-disease early identification test all the more emphatically identifies these malignant growth types.
“Malignant growths like prostate shed less DNA than different tumors, which is the reason existing screening tests are as yet significant for these diseases.”
In the mean time the consequences of NHS contemplates, including 165,000 patients, are normal by 2023, and on the off chance that results are positive, they would be extended to include around 1,000,000 members across 2024 and 2025.
______________________
Blood | Don’t forget to follow us on Twitter @njtimesofficial. To get latest updates