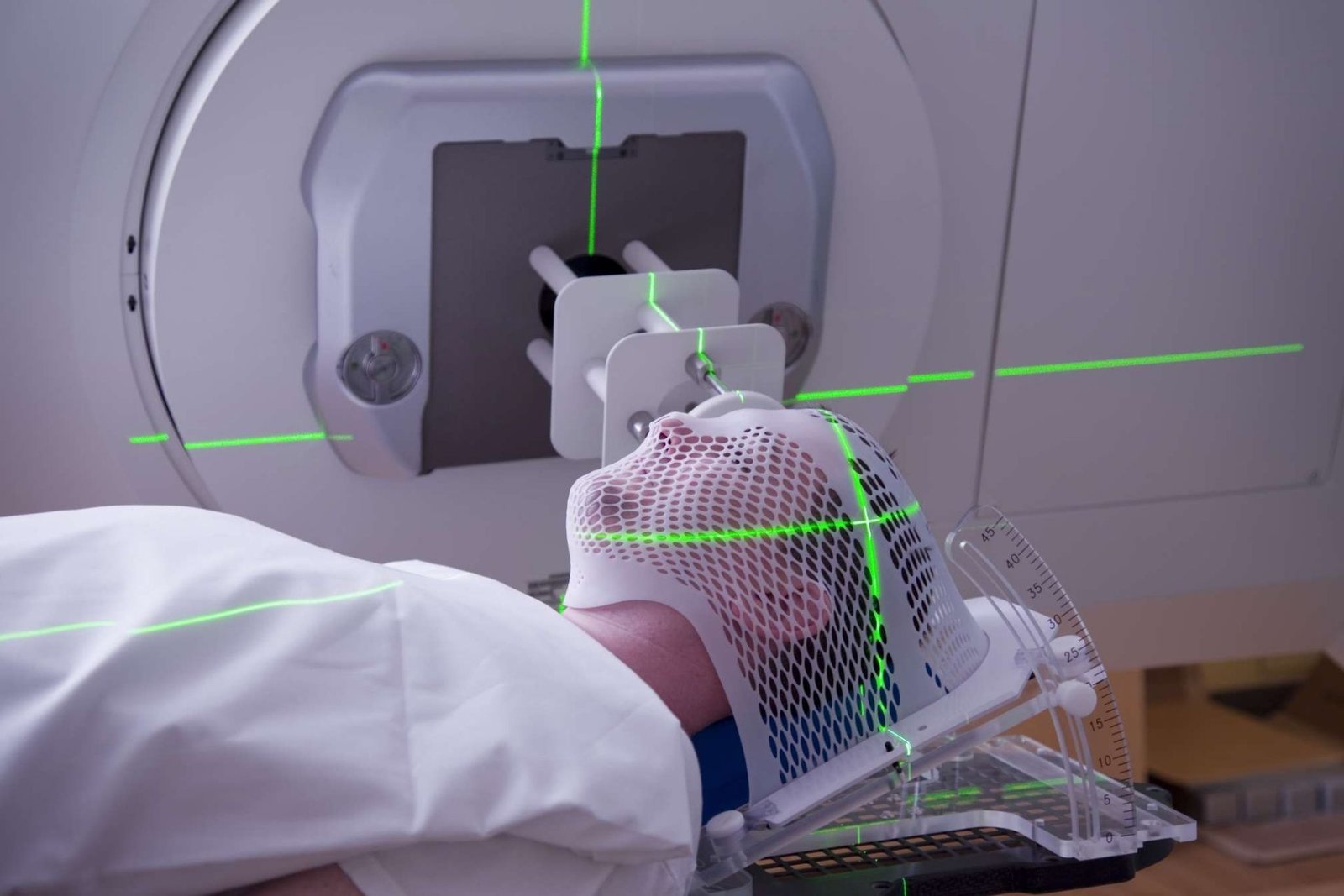
According to new research, a single dose of radiation therapy, which is typically used to treat cancer, can “reprogram” your heart into a younger and healthier version of itself. A more invasive procedure to correct electrical problems in the heart that cause arrhythmia, or irregular heartbeat, can be replaced by biological renovation.
Experiments on donated hearts from people who died or received transplants revealed that these benefits can appear a few days to weeks after the procedure and last for at least two years, according to a study published Sept. 24 in the journal Nature Communications.Further research in laboratory mice suggests that a lower dose of radiation can achieve the same effect, implying that this type of therapy could help people with a wide range of cardiac arrhythmias in a much shorter and noninvasive manner. The new study concentrated on people who had a condition known as refractory ventricular tachycardia (VT). Radiation therapy aided hearts in a matter of days to weeks.
The standard treatment for VT is catheter ablation, in which doctors insert a thin tube into the heart and burn the surrounding tissues. These “injuries” cause scarring over time, which blocks abnormal and overactive electrical signals that cause an irregular heartbeat.Researchers were surprised to learn that hearts with arrhythmias “experienced large improvements” after radiation therapy in a matter of days to weeks, as opposed to the months it takes for the more invasive procedure to work.

This is due to the fact that scar tissue takes time to form in the heart.This means that the radiation treatment works “just as well, if not better,” than the invasive procedure, even when there is no scarring.“We saw that scar tissue alone could not explain the remarkable clinical effects, implying that radiation improves the arrhythmia in some other way, so we dug into the details of that,” senior author and cardiologist Dr. Stacey Rentschler, an associate professor of medicine, developmental biology, and biomedical engineering at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, said in a statement. So, what could account for the clinical advantages?Radiation treatments, researchers discovered, caused heart muscle cells to begin expressing different genes, particularly those involved in a pathway known as “Notch.
” During early development, this pathway is critical in the formation of the heart’s electrical system. A single dose of radiation “temporarily activates” Notch, increasing the number of sodium ion channels in the heart; the more of these channels there are, the more likely the heart will beat normally.This is a significant discovery because Notch is typically turned off in adult hearts. As a result, researchers believe the therapy can make your heart “younger.”
“As part of the body’s response to that injury [from radiation therapy], cells in the injured portion of the heart appear to turn on some of these early developmental programmes to repair themselves,” said study co-author and radiation oncologist Dr. Julie Schwarz, a professor of radiation oncology at WashU Med, in a press release. “It’s critical to understand how this works because we can use that knowledge to improve how we treat these patients and then apply it to other diseases.”According to the team, Notch plays a significant role in reducing arrhythmias, but it is not the only player in the game.
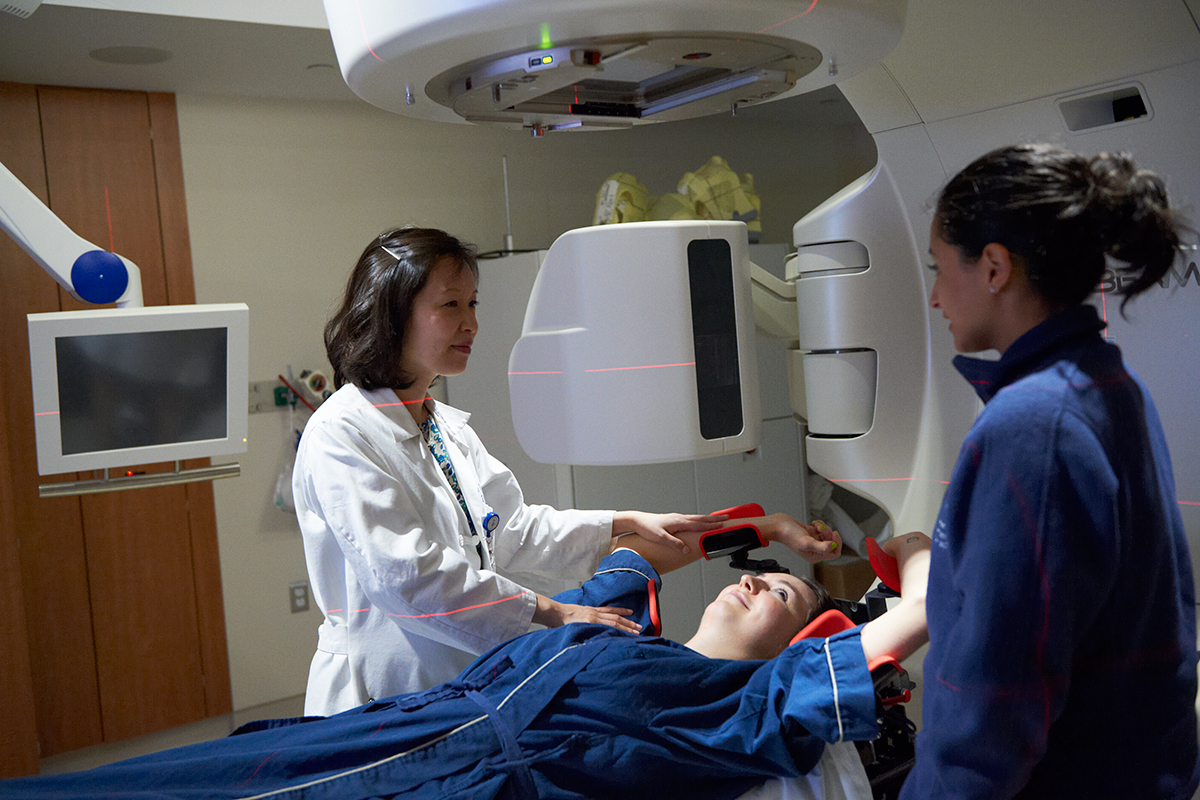
Future research will look into how and why radiation causes the heart to age and become a younger, healthier version of itself.
_________
Radiation Therapy | Don’t forget to follow us on Twitter @njtimesofficial. To get the latest updates